Table of Contents
Introduction
Monitoring webhook performance is crucial to ensure reliable and efficient communication between your software/application and external services, as delays or failures in webhook processing can lead to significant data loss or service disruptions. Additionally, performance monitoring helps identify bottlenecks and optimize the system, ensuring a smooth and responsive user experience.
In this article, we'll detail how to use the Telegraf agent to collect webhook performance statistics and forward them to a data source.
Getting Started with the Telegraf Agent
Telegraf is a plugin-driven server agent built on InfluxDB that collects and sends metrics/events from databases, systems, processes, devices, and applications. It is written in Go, compiles into a single binary with no external dependencies, and requires a minimal memory footprint. Telegraf is compatible with many operating systems and has many helpful output plugins and input plugins for collecting and forwarding a wide variety of system performance metrics.
Install Telegraf (Linux/Redhat)
/etc/telegraf/wget https://dl.influxdata.com/telegraf/releases/telegraf_1.30.0-1_amd64.deb
sudo dpkg -i telegraf_1.30.0-1_amd64.deb
RedHat/CentOS
wget https://dl.influxdata.com/telegraf/releases/telegraf-1.30.0-1.x86_64.rpm
sudo yum localinstall telegraf-1.30.0-1.x86_64.rpm
Configure an Output
You can configure Telegraf to output to various sources, such as Kafka, Graphite, InfluxDB, Prometheus, SQL, NoSQL, and more.
In this example, we will configure telegraf with a Graphite output. If you're not currently hosting your data source, start a 14-day free trial with Hosted Graphite by MetricFire to follow these next steps.
A Hosted Graphite account will provide the data source, offer an alerting feature, and include Hosted Grafana as a visualization tool.
To configure the Graphite output, locate the downloaded telegraf configuration file at /etc/telegraf/telegraf.conf and open it in your preferred text editor. Then, you will need to make the following changes to the file:
First, uncomment the line:
[[outputs.graphite]]
Next, uncomment and edit the server line to:
servers = ["carbon.hostedgraphite.com:2003"]
Finally, uncomment and edit the prefix line to:
prefix = "<YOUR_API_KEY>.telegraf"
Create an Example Webhook
This article assumes that you already have active webhook endpoints. If you you want to create a webhook endpoint and send requests to it for testing purposes, here's a quick guide on how to achieve this (Linux - Ubuntu 20.04):
- create a simple app that can receive requests to an endpoint
- configure a proxy server to handle/route requests to the app
- send requests to the endpoint
Launch a Flask App To Receive Requests
- dependencies: python
- pip install Flask
- create a file named app.py with the following:
from flask import Flask, request, jsonify
app = Flask(__name__)
@app.route('/webhook', methods=['POST', 'GET', 'PUT', 'DELETE'])
def webhook():
if request.method == 'POST':
data = request.get_json()
# Handle POST request
return jsonify({'message': 'POST request received', 'data': data}), 200
elif request.method == 'GET':
# Handle GET request
return jsonify({'message': 'GET request received'}), 200
elif request.method == 'PUT':
data = request.get_json()
# Handle PUT request
return jsonify({'message': 'PUT request received', 'data': data}), 200
elif request.method == 'DELETE':
# Handle DELETE request
return jsonify({'message': 'DELETE request received'}), 200
if __name__ == '__main__':
app.run(host='0.0.0.0', port=80)
Default port is usually 80, as long as it's not being used by another service or process.
Now you can run the flask app to listen for incoming webhooks: python app.py
Configure Nginx To Route Requests to the Flask App
- install nginx: sudo apt install nginx -y
- modify the default configuration file (generally located at: /etc/nginx/sites-available/default)
- add the following code-block within the server {} block of the default nginx conf file:
location /webhook {
proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1:80;
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Proto $scheme;
}
- check the syntax of the file: sudo nginx -t
- restart nginx: sudo service nginx restart
Send Requests To the Flask App
-
curl -X POST http://localhost/webhook -H "Content-Type: application/json" -d '{"key1":"value1", "key2":"value2"}'
-
curl -X GET http://localhost/webhook
-
curl -X PUT http://localhost/webhook -H "Content-Type: application/json" -d '{"key1":"value1", "key2":"value2"}'
-
curl -X DELETE http://localhost/webhook
You should now be able to see the requests hitting the webhook endpoint in your Flask app, e.g: 127.0.0.1 - - [26/Jun/2024 16:05:40] "POST /webhook HTTP/1.0" 200 -
Configure the Telegraf Plugin
Telegraf has many input plugins that can collect a wide range of data from many popular technologies and 3rd party sources. In this example, we'll demonstrate how to collect and forward metrics from your webhook endpoints.
You will need to search for the inputs.http_response section in your telegraf.conf file, uncomment the [[inputs.http_response]] line.
Then you will define your webhook endpoint URL(s) and add similar sections for each request type:
[[inputs.http_response]]
urls = ["http://localhost/webhook"]
method = "POST"
[[inputs.http_response]]
urls = ["http://localhost/webhook"]
method = "GET"
[[inputs.http_response]]
urls = ["http://localhost/webhook"]
method = "PUT"
[[inputs.http_response]]
urls = ["http://localhost/webhook"]
method = "DELETE
Finally, you can run the telegraf daemon using the following command, which will help you see if there are any configuration errors in the output:
telegraf --config telegraf.conf
Telegraf will now forward about 4 metrics (per host/method/webhook-endpoint/status-code), to your configured datasource. This is what the metrics look like in the Graphite format:
telegraf.<host>.<method>.success.<endpoint>.<status>.http_response.content_length
telegraf.<host>.<method>.success.<endpoint>.<status>.http_response.http_response_code
telegraf.<host>.<method>.success.<endpoint>.<status>.http_response.response_time
telegraf.<host>.<method>.success.<endpoint>.<status>.http_response.result_code
See the official GitHub repository for additional details and configuration options for the http_response plugin.
Use Hosted Graphite by MetricFire to Create Custom Dashboards and Alerts
MetricFire is a monitoring platform that enables you to gather, visualize and analyze metrics and data from servers, databases, networks, processes, devices, and applications. Using MetricFire, you can effortlessly identify problems and optimize resources within your infrastructure. Hosted Graphite by MetricFire removes the burden of self-hosting your monitoring solution, allowing you more time and freedom to work on your most important tasks.
Once you have signed up for a Hosted Graphite account and used the above steps to configure your server(s) with the Telegraf Agent, metrics will be forwarded, timestamped, and aggregated into the Hosted Graphite backend.
-
Metrics will be sent and stored in the Graphite format of: metric.name.path <numeric-value> <unix-timestamp>
-
The dot notation format provides a tree-like data structure, making it efficient to query
-
Metrics are stored in your Hosted Graphite account for two years, and you can use them to create custom Alerts and Grafana dashboards.
Build Dashboards in Hosted Graphite's Hosted Grafana
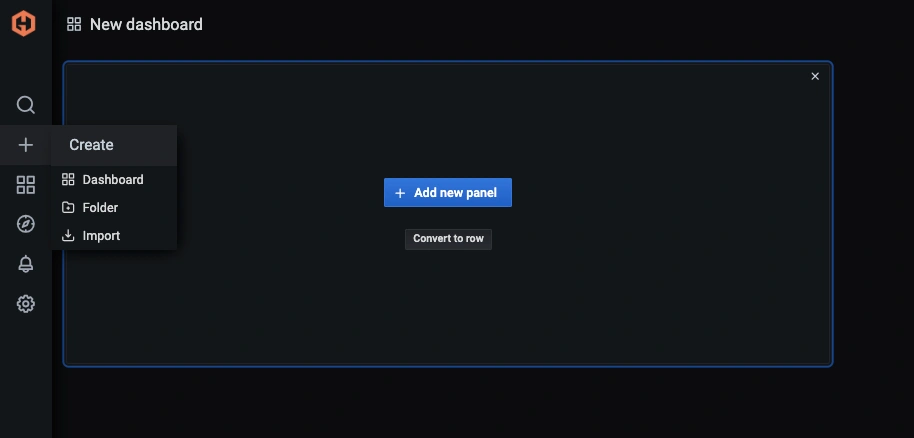
In the Hosted Graphite UI, navigate to Dashboards => Primary Dashboards and select the + button to create a new panel:
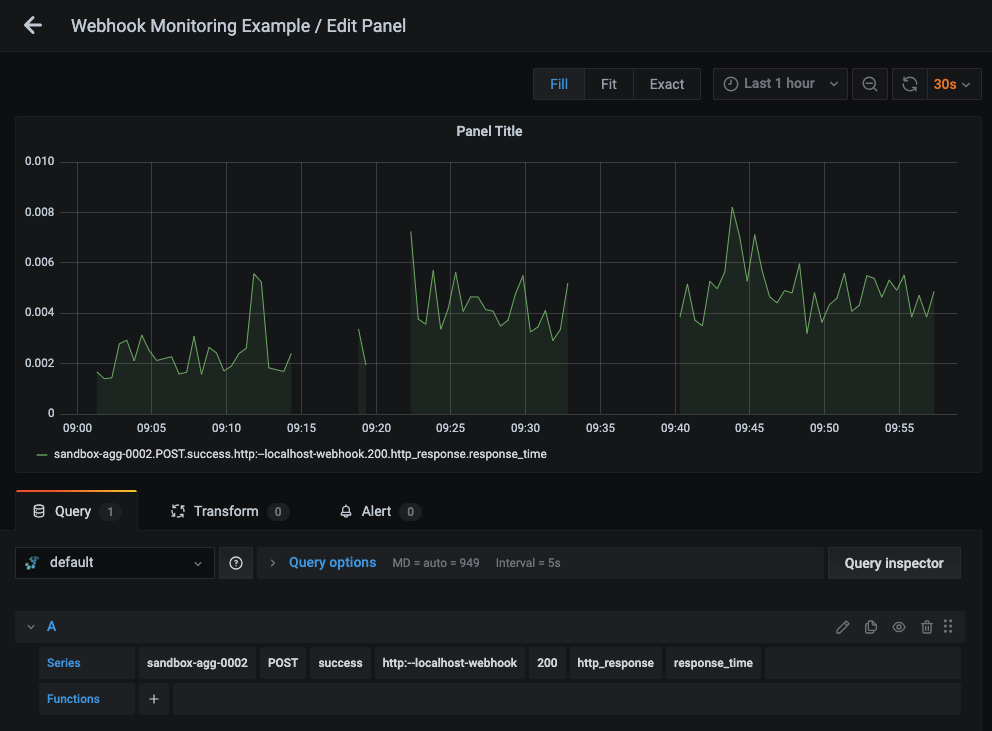
Then you can use the query UI in Edit mode to select a graphite metric path (the default data source will be the hosted graphite backend if you are accessing Grafana via your HG account):
NOTE: The Hosted Graphite datasource also supports wildcard (*) searching to grab all metrics that match a specified path.
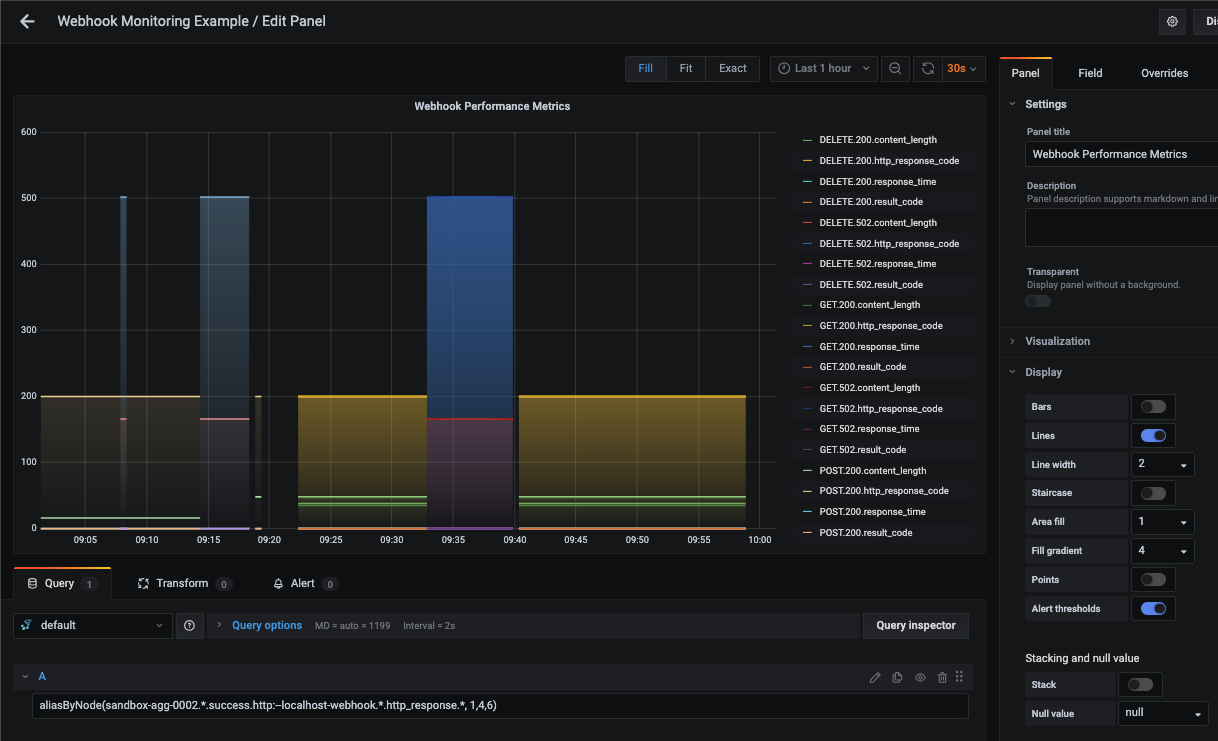
Now you can apply Graphite functions to these metrics like aliasByNode() to format the name:
Grafana has many additional options to apply different visualizations, modify the display, set units of measurement, and some more advanced features like configuring dashboard variables and event annotations.
The above example has a dashboard variable configured for 'instance' at index 4 of the metric series. See the Hosted Graphite dashboard docs for more details.
Creating Graphite Alerts
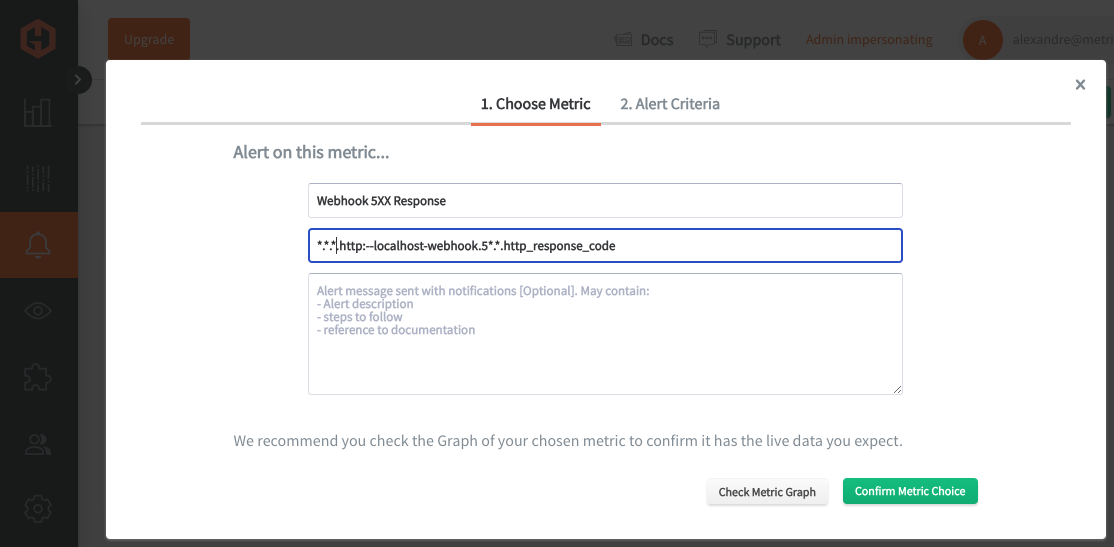
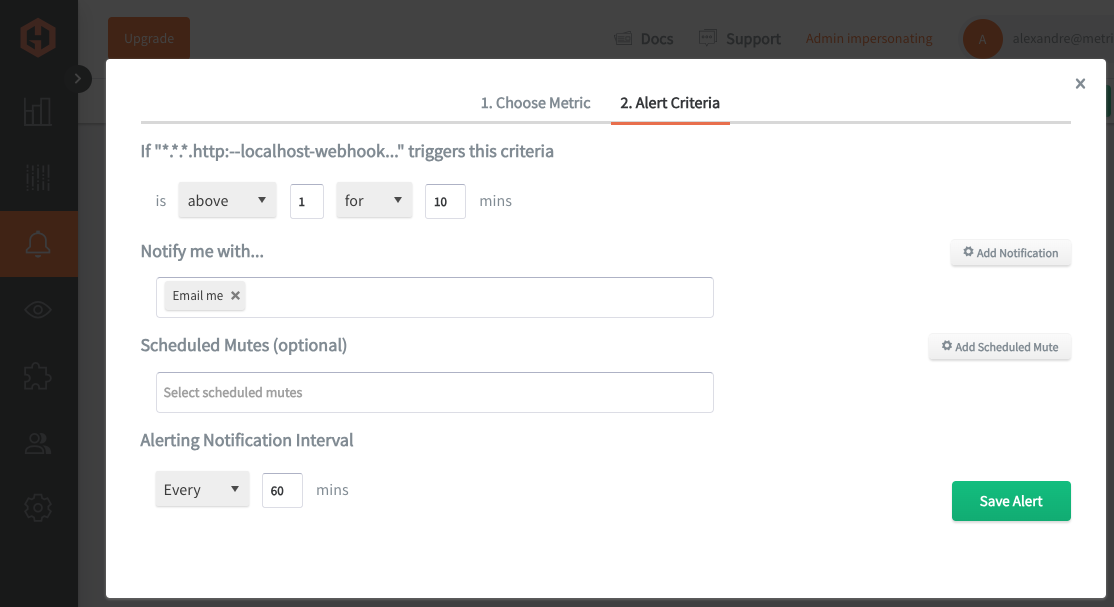
In the Hosted Graphite UI, navigate to Alerts => Graphite Alerts to create a new alert. Name the alert, add a query to the alerting metric field, and add a description of what this alert is:
Then, select the Alert Criteria tab to set a threshold and select a notification channel. The default notification channel will be the email you used to sign up for the Hosted Graphite account. Still, you can easily configure channels for Slack, PagerDuty, Microsoft Teams, OpsGenie, custom webhooks and more. See the Hosted Graphite docs for more details on notification channels:
Conclusion
Monitoring your webhook endpoints is essential to maintain operational efficiency and customer satisfaction, as any downtime or performance issues can directly impact critical business processes and user interactions. Moreover, proactive monitoring allows for quick detection and resolution of issues, minimizing potential revenue loss and preserving the company's reputation for reliability and service quality.
Tools like dashboards and alerts will complement your data by providing real-time visualization, proactive identification of issues, historical trend analysis, and facilitating informed decision-making, all essential for maintaining a robust and efficient infrastructure.
Sign up for the free trial and begin monitoring your infrastructure today. You can also book a demo and talk to the MetricFire team directly about your monitoring needs.